Description
product information
WHAT ARE INDUSTRIAL RECTIFIERS – BATTERY CHARGERS?
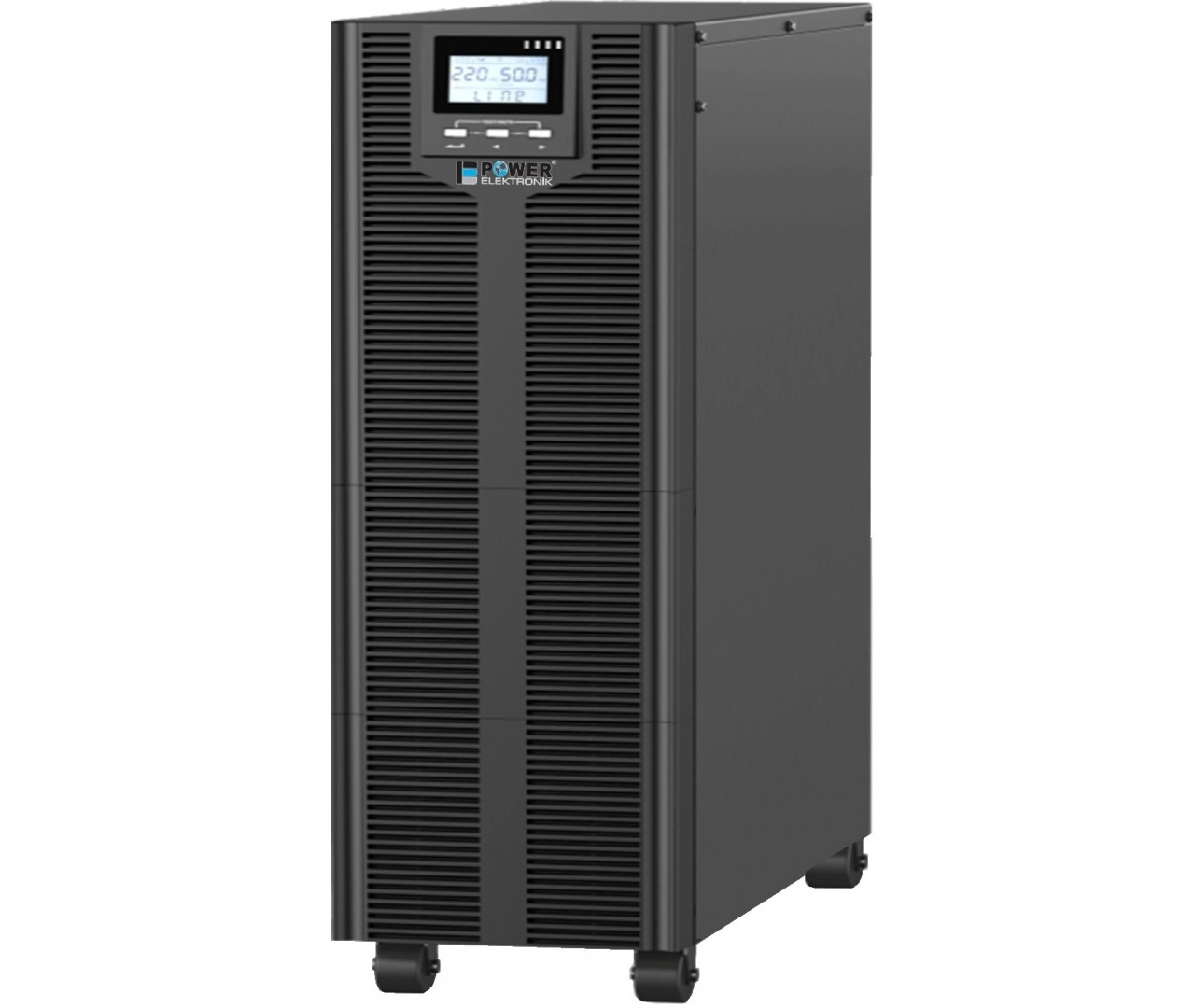
Rectifier products are used in high voltage (HV), medium voltage (MV) and low voltage (LV) power control and automation systems to meet requirements such as relay control, circuit breaker control, communication, automatic control and emergency lighting during power failure or restoration. These products are designed for battery backup.
HOW DOES AN INDUSTRIAL RECTIFIER WORK?
Industrial rectifiers take 1-phase or 3-phase AC mains energy, reduce it to the desired level using a step-down transformer, while delivering the required energy to the thyristor circuits in the rectifier circuit by providing galvanic isolation. The DC energy exiting the rectifier unit is filtered and converted into smoother and cleaner DC energy.
With the help of the rectifier software, this DC energy charges the batteries according to the Float-Boost-Equalizing charging modes and supplies the required continuous energy to DC loads.
In the event of a power outage, it supplies all its DC power needs from the batteries. The batteries continue to supply DC loads according to the programmed discharge level for a pre-calculated period of time (e.g. 4, 6, 8, 12 hours). When the mains is restored, the discharged batteries start charging.
WHERE ARE INDUSTRIAL RECTIFIERS – BATTERY CHARGERS USED?
» In power plants (hydro, thermal, energe, geothermal, biomass, natural gas, etc.)
» HV high voltage transmission and derivation centers
» MV medium voltage transformers and distribution centers
» Energy control centers of subway stations
» In control and command centers of all types of pipeline stations
» DCS, Scada automation systems
WHY ARE THERE TYPES WITH 24, 48, 110, 220 VDC?
The coil control voltage of electrical devices such as relays and circuit breakers controlled by industrial rectifiers are designed for different voltages by different manufacturers.
Generally, a low voltage 24 VDC rectifier is used for low power DC loads.
Since it is rated as 48 VDC, 110 VDC and 220 VDC to allow compact designs at lower currents for DC control devices that draw higher power current, the rectifier design will also be installed according to this DC voltage.
HOW DO I SIZE RECTIFIER BATTERIES?
In industrial rectifiers, the battery types may sometimes be lead-acid or nickel-cadmium batteries depending on need, sometimes preference and sometimes specification.
While OPZV tubular plate batteries are preferred where high current is required immediately, OPZS and VRLA types are preferred in systems requiring a long discharge time. Ni-Cd batteries may be preferred where high performance over many years and less temperature effects are desired.
When calculating battery capacities, the required DC energy is determined by extracting the load profile (current and duration information) and using the IEEE battery calculation method.
Rectifier products are used in high voltage (HV), medium voltage (MV) and low voltage (LV) power control and automation systems to meet requirements such as relay control, circuit breaker control, communication, automatic control and emergency lighting during power failure or restoration. These products are designed for battery backup.
HOW DOES AN INDUSTRIAL RECTIFIER WORK?
Industrial rectifiers take 1-phase or 3-phase AC mains energy, reduce it to the desired level using a step-down transformer, while delivering the required energy to the thyristor circuits in the rectifier circuit by providing galvanic isolation. The DC energy exiting the rectifier unit is filtered and converted into smoother and cleaner DC energy.
With the help of the rectifier software, this DC energy charges the batteries according to the Float-Boost-Equalizing charging modes and supplies the required continuous energy to DC loads.
In the event of a power outage, it supplies all its DC power needs from the batteries. The batteries continue to supply DC loads according to the programmed discharge level for a pre-calculated period of time (e.g. 4, 6, 8, 12 hours). When the mains is restored, the discharged batteries start charging.
WHERE ARE INDUSTRIAL RECTIFIERS – BATTERY CHARGERS USED?
» In power plants (hydro, thermal, energe, geothermal, biomass, natural gas, etc.)
» HV high voltage transmission and derivation centers
» MV medium voltage transformers and distribution centers
» Energy control centers of subway stations
» In control and command centers of all types of pipeline stations
» DCS, Scada automation systems
WHY ARE THERE TYPES WITH 24, 48, 110, 220 VDC?
The coil control voltage of electrical devices such as relays and circuit breakers controlled by industrial rectifiers are designed for different voltages by different manufacturers.
Generally, a low voltage 24 VDC rectifier is used for low power DC loads.
Since it is rated as 48 VDC, 110 VDC and 220 VDC to allow compact designs at lower currents for DC control devices that draw higher power current, the rectifier design will also be installed according to this DC voltage.
HOW DO I SIZE RECTIFIER BATTERIES?
In industrial rectifiers, the battery types may sometimes be lead-acid or nickel-cadmium batteries depending on need, sometimes preference and sometimes specification.
While OPZV tubular plate batteries are preferred where high current is required immediately, OPZS and VRLA types are preferred in systems requiring a long discharge time. Ni-Cd batteries may be preferred where high performance over many years and less temperature effects are desired.
When calculating battery capacities, the required DC energy is determined by extracting the load profile (current and duration information) and using the IEEE battery calculation method.
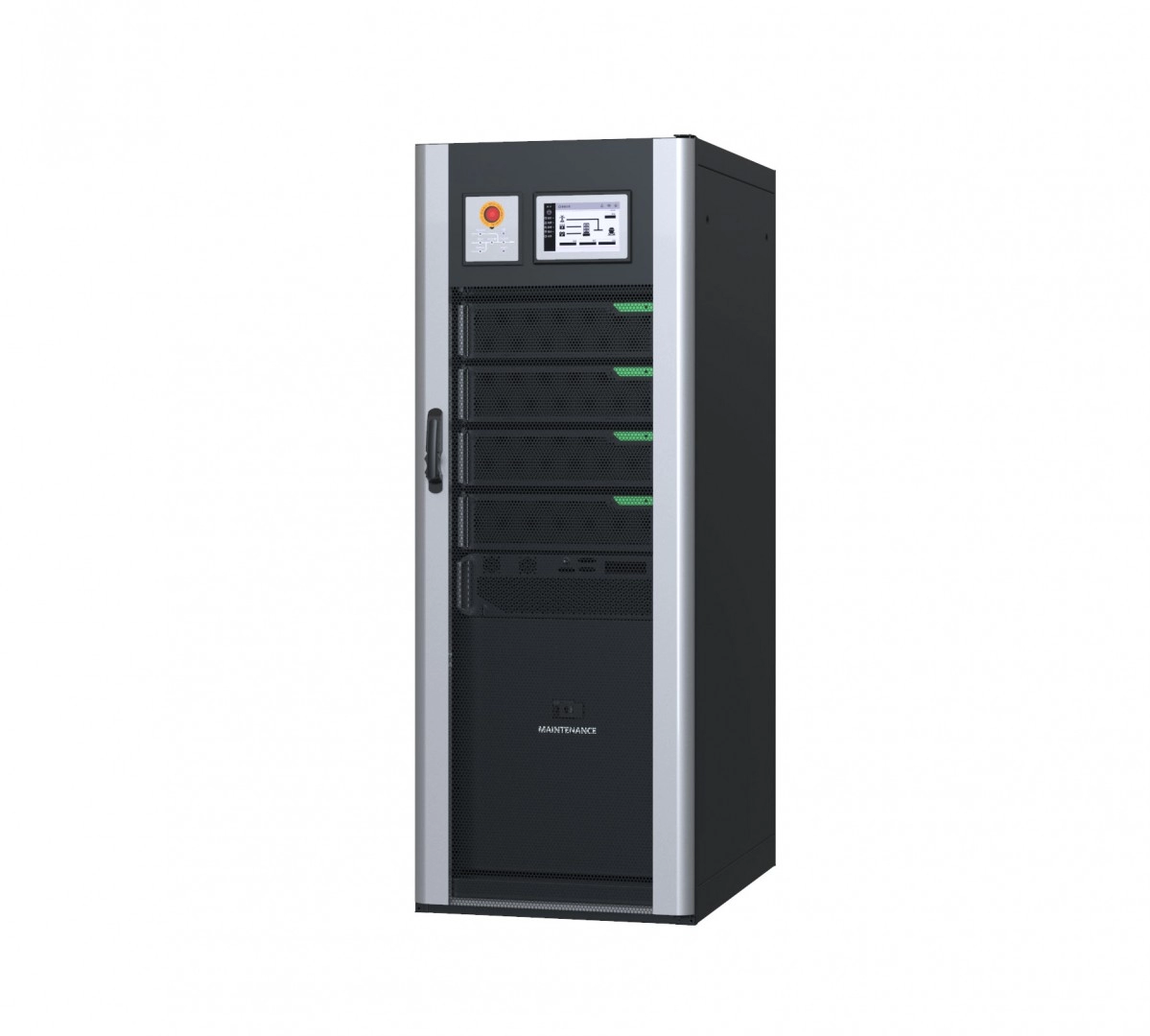
WHEN ARE RECTIFIERS USED AS A REDUNDANT BACKUP?
Especially in facilities where power outages can have serious consequences, if one of the rectifiers fails, it is preferable to use the other rectifier-battery set in parallel with the backup power supply to continue to meet DC power needs without interruption.
Especially in facilities where power outages can have serious consequences, if one of the rectifiers fails, it is preferable to use the other rectifier-battery set in parallel with the backup power supply to continue to meet DC power needs without interruption.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.